Anoxic Brain Injury
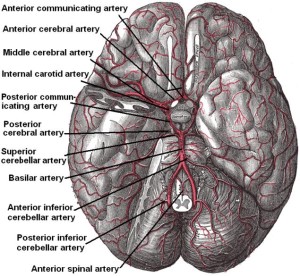
Cerebral anoxia is associated when there is deterioration in brain function as a result of a disruption in the brain’s vascular system. It is said, that an “anoxic brain injury can cause diffuse injury to the brain resulting in widespread neurological, behavioural and cognitive impairments.” The brain requires oxygen for it to properly function. When the brain is not receiving oxygen, or very little oxygen, for four minutes or longer, brain cells begin to die. After five minutes, permanent anoxic brain injury can occur. Anoxic brain injury also known as cerebral hypoxia, is serious and life-threatening. The injury can cause disabilities and cognitive problems that could change the victim’s life. When the brain cells begin to die, it interrupts the brain’s electrochemical impulses and causes problems with the performance of neurotransmitters–the chemical messengers that transmit messages within the brain. These regulate body functions and influence behavior. They also play a major role in memory.
Table of Contents
Causes of Anoxic Brain Injury
- Respiratory arrest
- Electrical shock
- Drowning
- Heart attack
- Brain tumors
- Heart arrhythmia
- Extreme low blood pressure
- Carbon monoxide inhalation
- Poisoning
- Choking
- Compression of the trachea
- Respiratory conditions which interfere with proper breathing
- Suffocation
- Illegal drug use
Symptoms of Anoxic Brain Injury
The injury usually (but not always) begin with unconsciousness or a coma. After a period of unconsciousness the person may fall into a vegetative state–they aren’t in a coma but they can respond when stimulated. If the person survives these stages and regain full consciousness, they may experience a wide variety of symptoms that could be similar to a traumatic brain injury (TBI). The symptoms can vary depending on the damage that was done to the brain and where the injury occurred. The victim may also suffer cognitive and physical problems from anoxia. These could include: Short term memory loss: The person cannot remember new information that had just been presented. The part of the brain that is responsible for learning new information is very sensitive to lack of oxygen. Executive functions are weakened: Executive functions include decision making, reasoning, and processing information. They may become impulsive or indecisive and cannot focus on a single task. Anomia: This term is used to describe the process of understanding and using words. It may be difficult to remember the right word to use in a certain instance. They may not understand common words or use antonyms instead of the correct word. Visual Issues: The victim may have trouble processing visual information. Depth perception is often skewed and line of sight might be off causing them to reach for something in the wrong direction. It can sometimes result in cortical blindness. The patient may still think they can see but they won’t be able to identify certain objects, colors, or shapes. The brain does not realize that it is damaged. Ataxia: Lack of coordination. They may not be able to walk properly and wobble as they try to do so. Apraxia: Not being able to complete common tasks. These could include brushing teeth or drinking from a cup. Movement problems: Patients could have muscle spasms and have involuntary body movements. Brain dysfunction: Patients could suffer from confusion, depression, hallucinations, delusions, personality changes, and inability to concentrate.
Treatment for Anoxic Brain Injury
Recovering from such an injury is very difficult to do. The amount of damage as well as where the damage occurred will determine if or how the patient will recover. The length of time spent unconscious with the amount of normal function that returns after the first month of the injury, can also indicate the chance of long-term recovery. Recovery may takes months or years. People who have suffered from a mild anoxic brain injury have a better chance of fully or near full recovery. The longer time spent unconscious the greater chance of brain death. If the patient awakens from the unconscious period, they may go through different types of therapy to get the victim to return to normal such as:
- Speech therapy
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Recreational therapy
- Adaptive equipment therapy
Preventing Anoxic Brain Injury
Preventing anoxic brain injuries can be difficult because accidents do happen. However, the following are some suggestions to reduce the risk of anoxic brain injuries:
- Make sure choking hazards are out of reach from children
- Chew your food completely
- Learn how to swim and teach your children to swim
- Learn and certification in CPR
- Avoid high-voltage electrical sources
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home
- Do not abuse drugs
- Keep up on your cardiac health by exercising often and monitoring your blood pressure
If you or someone you know have suffered from an anoxic brain injury due to someone else’s negligence, contact Christensen & Hymas at (801)506-0800 for a free confidential consultation.
Image “Arteries beneath brain Gray closer” courtesy of Wikid77. The image is in the public domain.
Free Consultation
Learn your Rights. Get Answers. Free.
